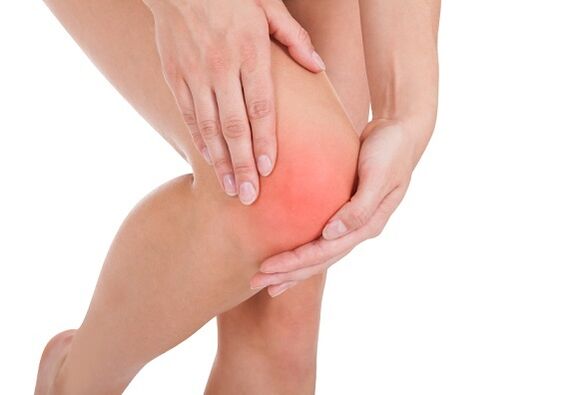
Knee pain is one of the most common unpleasant sensations that every person has experienced at least once. The progression of diseases, which may cause pain, is due to the fact that the human knee is made up of many structures and, every day, all of them are subject to colossal loads. The damage can affect one of the ligaments or tendons, or specific sacs that fill with fluid, as well as cartilage. This symptom can be a sign of illnesses not only related to the knee, but also general illnesses of the body or systems.
It is also necessary to distinguish with which movements the pain occurs, for example, knee pain during flexion is inherent in people who lead an active lifestyle and often speaks of a violation of the structure of joints and bones. These spasms appear mainly in the more advanced stages of the disease course, when it is impossible to do without treatment with the aid of surgical intervention. Knees often sore and crack when squatting, this can indicate that cartilage tissue is being effaced (mostly seen in athletes due to constant running). The pain inside arises due to various pathologies of the joint or the occurrence of neoplasms. The onset of pain after childbirth is due to the fact that, during pregnancy, the female body has gone through many changes, which can lead to the development of some diseases.
It is important to determine why the pain in the knee joint manifests itself, because some ailments can only be cured with the help of operable intervention, and for some it will be sufficient to use traditional medicine.
Etiology
As mentioned above, there are many reasons why knees hurt and they are not always directly related to injuries, illnesses and bruises in the knee joint. The first group of factors is formed by disorders that directly affect the knee joint, including:
- Goonarthrosis is a disease that most commonly affects people over forty. The condition usually affects both knees. The main symptom is pain and crushing during the extension and squat. Spasms are sharp and sharp. The degree of intensity decreases at bedtime;
- bring blood to the joint cavity;
- Meniscal damage can occur at any age, regardless of gender. Often only one knee is affected. This disease is characterized by the manifestation of severe crushing and pain in the knee when bending or after running. In addition, the person loses the ability to move because he feels unbearable pain at the slightest movement of the leg;
- arthritis - the disorder develops very quickly, the inflammatory process spreads to the knee joints of both legs. It is best to start treatment as soon as possible because the disease has spread to other joints;
- Violation of the integrity of the ligaments due to rupture, most of the times the internal ligament is susceptible to this, much less occurs laterally. In this case, there is swelling and limitation of motor functions;
- various tendon inflammations - the appearance of which is due to various reasons, for example, infectious diseases or bacterial influence, trauma or bruises, drug allergies or abnormalities in the body structure. In such disorders, the pain in the knee is expressed from within;
- dislocation or dislocation of the patella - it occurs very rarely and mainly in children or athletes, after intense effort or running;
- inflammatory process in the joint pouch. In case of inappropriate treatment, complications may arise, which should only be eliminated with the aid of medical intervention;
- pathological processes in the synovial membrane covering the joint;
- the occurrence of a cyst on the inside of the knee joint causes pain under the knee in the back;
- destruction of the integrity of the adipose tissue covering the joint. Externally, this manifests itself in the form of swelling of the injured knee;
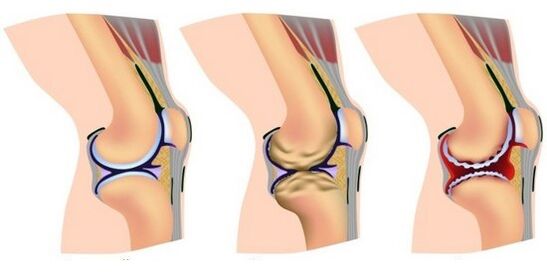
- osteoarthritis, in which cartilage tissue becomes thinner;
- various infectious diseases whose course can lead to arthritis. Knee pain is expressed when walking as well as after squats;
- bone tuberculosis;
- spinal pathologies cause a feeling that the knee pains when walking;
- metabolic disturbances or salt deposition in the knee often cause pain in the knees during squats.
The second group of reasons is composed of other influences from which knee joint pain arises:
- excessively high body weight;
- external injuries or bruises to the knee joint;
- the working conditions in which the person is required to remain standing for several consecutive hours;
- intense physical activity - that's why this disorder is more observed in professional athletes, for example, after running;
- incorrect posture while working;
- wearing uncomfortable high-heeled shoes.
There are several reasons a woman's knees hurt during pregnancy:
- an increase in body weight (in some cases up to twenty kilograms);
- lack of calcium and other minerals in the body;
- production of a specific hormone that softens the ligament tissue.
After delivery, all unpleasant sensations should disappear by themselves, but if they don't, consult a doctor as this may be an indication of the above illnesses. After childbirth, a woman may experience pain in her knees as she squats, rises, and stretches. This is due to the following reasons:
- intensive muscle work during childbirth;
- a sudden involuntary movement during the birth of a baby can cause dislocation;
- whether a woman had multiple musculoskeletal system disorders prior to delivery;
- when breastfeeding a baby, fluid builds up in the female body, which damages the joints, which is why pain is felt when lifting and extending the knees.
Symptoms
In addition to the pronounced signs - pain of variable intensity and crunching when crouching, this manifestation presents additional symptoms characteristic of the disease, which made the knee pain when walking or other leg movements:
- sleep disorders;
- increase in body temperature;
- decreased or complete lack of appetite;
- rigidity of movement;
- increased pain when walking. There is a marked improvement in the sitting or lying position;
- noticeable swelling of the injured knee - may be seen from the inside;
- inability to transfer weight to a sore limb;
- deformation of the patella;
- change in skin color on the knee;
- fever.
When expressing the first signs, you should immediately contact a medical institution for diagnosis and to schedule an effective treatment.
Diagnosis
Since many disorders cause knee pain when walking, after running, squatting and standing, the diagnosis should consist of:
- a detailed survey of the patient for the appearance of the first symptoms, the intensity of the pain, the place of its onset (outside or inside), possible causes (for example, when walking, after running or giving birth), which causes pain ;
- palpation of the knee by the treating physician to obtain a more complete picture of the location of pain as well as to identify swelling;
- analysis of patient blood for general and biochemical research;
- radiography - in which any pathology of the knee structure will be clearly visible;
- puncture fluid collection - performed if the treating physician suspects bone tuberculosis;
- fluid puncture of the knee joint;
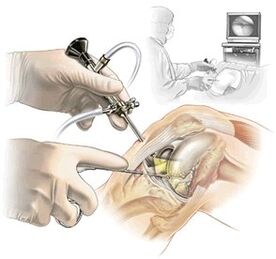
- arthroscopy - performed in cases of meniscal injury that causes pain in the knee from the inside. This method is performed not only for diagnosis but also during treatment;
- measure bone tissue density;
- Knee ultrasound;
- patient examinations by means of magnetic resonance and computed tomography.
Treatment
There is no single way to cure all diseases and disorders. The method of treatment for each patient is prescribed individually and depends on the cause of the onset and the severity of the spasms, whether the knee is painful when walking, after running, squatting or standing. Treatment methods that are prescribed to all patients without exception, including postpartum women:
- reducing the load on the lower extremities so that minor symptoms do not appear;
- the imposition of a fixation bandage on the injured knee;
- warm the knee with ointments or warming compresses. As prescribed by the physician, cold compresses are used, but no more than fifteen minutes a day;
- anti-inflammatory drugs.
If necessary, treatment is carried out with surgical intervention.
In addition, there are alternative therapies that can reduce the onset of symptoms, but they can only be used after consulting a doctor. These pain treatments include:
- iodine mesh;
- a compress of your own urine;
- a mixture of raw potato and kerosene;
- apple cider vinegar lotions mixed with egg yolk;
- horseradish chopped potato ointment;
- an onion compress, for this you need to cut it in half and apply it in half on the outside and inside of the knee;
- cologne and dandelion solution;
- tinctures of elecampane root and alcohol;
- a compress of black elderberry, chamomile and pine cake;
- marigold lotion;
- a mixture of mustard and honey.
Folk remedies are not recommended for women during pregnancy and after childbirth, when the baby is breastfeeding.
Prophylaxis
To avoid knee pain when walking, after running or squatting, you need to:
- adhere to a healthy lifestyle;
- always monitor your posture;
- maintain your own normal body weight;
- warm up your muscles before training so that your knees don't spasm after running and exercising;
- wear only comfortable shoes;
- promptly treat all illnesses that can lead to this disorder;
- undergo a routine examination at the clinic several times a year;
- perform gymnastics if a person's lifestyle or working conditions are standing or sitting;
- avoid hypothermia;
- at the first symptoms, especially after childbirth or running, consult a doctor.